The Ocean and Its Wonders/Chapter 13

CHAPTER XIII.
MISCELLANEOUS PHENOMENA OF THE POLAR SEAS AND REGIONS—THE AURORA BOREALIS—ICE-BLINK—OPTICAL ILLUSIONS—ANECDOTE OF SCORESBY—HALOS—CORONÆ—MOCK SUNS—REFRACTION—FROSTS.
![]() wing to the intensity of the cold in the arctic regions, there are, as we may readily believe, many singular appearances connected with the ocean and the atmosphere, which are worthy of special notice.
wing to the intensity of the cold in the arctic regions, there are, as we may readily believe, many singular appearances connected with the ocean and the atmosphere, which are worthy of special notice.
Chief, perhaps, among the phenomena of those regions is the Aurora Borealis.
Ever mindful of the welfare of the creatures whom he has formed, the Almighty has appointed a light to mitigate the darkness of the polar regions when the sun, in its appointed course, withdraws for a season.
What the aurora borealis is no one knows, although many have hazarded opinions regarding it. What it is like is known even to ourselves, though the faint indications of it which sometimes beam in our own heavens are not to be compared to the brilliancy of the spectacle that is occasionally presented in the northern skies.
The most ordinary aspect of the aurora is that of a band of pale-green light extending irregularly over part of the sky, and marked by wavy motions, as well as by varying brightness. Sometimes one

AURORA BOREALIS.
part of this band becomes more bright than another part. Sometimes the whole seems to move gently, like the undulations of a flag in a light breeze; at other times more vigorous action takes place, and pointed tongues of light shoot vividly up into the zenith. This sometimes takes place so frequently, and the tongues are so long and numerous, that the aurora has been popularly termed the "northern streamers."
Although pale-green is the most frequent colour, the aurora borealis has often been observed with blue and red hues; and the sky has been seen suffused with an intense crimson colour by it.
Captains Parry and Lyon saw these northern lights in full splendour during their residence in the arctic regions. They tell us that "the aurora had a tendency to form an irregular arch, which, in calm weather, was very often distinct, though its upper boundary was seldom well defined; but whenever the air was agitated, showers of rays spread in every direction with the rapidity of lightning, but always appearing to move to and from a fixed point, somewhat like a ribbon held in the hand and shaken with an undulatory motion. No rule, however, could be traced in the movement of those lighter parcels called the 'merry dancers,' which flew about perpetually towards every quarter; becoming in stormy weather more rapid in their motions, and sharing all the wildness of the blast. They gave an indescribable air of magic to the whole scene, and made it not wonderful that, by the untaught Indian, they should be viewed as 'the spirits of his fathers roaming through the land of souls.'"
We are told by some that the aurora borealis is accompanied by a loud hissing and crackling sound; and Captain Lyon says that the sudden glare and rapid bursts of those wondrous showers of fire make it difficult to believe that their movements are wholly without sound. Yet such would seem to be the case, for the same authority tells us that he stood on the ice for hours listening intently and could hear nothing. He was thoroughly convinced that no sound proceeds from the aurora, and most intelligent voyagers support him in this opinion.
That the aurora dims the lustre of the stars seen through it, is a fact which was ascertained clearly by the same gentleman; and that it moves in a region beyond the clouds is also evident from the fact that when the latter covered the sky the aurora disappeared.
But some of the most singular appearances of the sea and sky in the polar regions are presented in summer. During that season the perpetual presence of the sun and the large tracts of ice floating about on the sea exert their opposing influences so as to produce the most astonishing results.
One part of the sea being covered with ice, produces a cold atmosphere; another part being free from ice, produces a warmer atmosphere. Refraction is the result of viewing objects through those different media, and very curious appearances follow. When Scoresby was in Greenland a singular atmospheric phenomenon occurred, whereby he became aware of the approach of his father's ship some time before it rose above the horizon. He had reached Greenland before his father, who followed him in the Fame. The following is his account of the circumstance:—
"On my return to the ship, about eleven o'clock, the night was beautifully fine and the air quite mild. The atmosphere, in consequence of the warmth, being in a highly refractive state, a great many curious appearances were presented by the land and icebergs. The most extraordinary effect of this state of the atmosphere, however, was the distinct inverted image of a ship in the clear sky, over the middle of the large bay or inlet, the ship itself being entirely beyond the horizon. Appearances of this kind I have before noticed, but the peculiarities of this were the perfection of the image, and the great distance of the vessel that it represented. It was so extremely well defined, that, when examined with a telescope, I could distinguish every sail, the general 'rig of the ship' and its peculiar character; insomuch that I confidently pronounced it to be my father's ship the Fame, which it afterwards proved to be, though, on comparing notes with my father, I found that our relative positions at the time gave our distance from one another very nearly thirty miles, being about seventeen miles beyond the horizon, and some leagues beyond the line of direct vision."
Scoresby was, perhaps, one of the most persevering and intelligent observers of nature that ever went to the polar seas. His various accounts of what he saw are most interesting. We cannot do better than quote his remarks upon ice-blink, that curious appearance of white light on the horizon, whereby voyagers are led to infer the presence of ice:—
"This appearance of the ice-blink" says he, "occurred on the 13th of June 1820, in latitude 76° north. The sky aloft was covered with dense, uniform, hazy cloud, which indeed occupied the whole of the heavens, excepting a portion near the horizon, where it seemed to be repelled. The upper white blink referred to ice about six miles distant, being beyond the horizon; the narrow yellowish portions referred to floes and compact ice; the lowest yellow blink, which in brightness and colour resembled the moon, was the reflection of a field at the distance of thirty miles, to which, directed by the blink, we made way in the Baffin, through the channels of water represented in the sky by bluish-gray streaks. The field we found to be a sheet of ice 150 miles in circumference!"
Another very singular appearance observed occasionally in foggy weather is a series of bright circles, or coronæ, surrounding the heads or persons of individuals in certain positions. We have, while standing at the mast-head of a vessel in Hudson's Straits, observed our own shadow thrown on the sea with a bright halo round it. The day was bright and hazy at the time. Referring to a particular case of this kind, Scoresby says:—
"During the month of July 1820, the weather being often foggy, with a bright sun sometimes shining at the height of the day, some extraordinary coronæ were observed from the mast-head. These occurred opposite to the sun, the centre of all the circles being in a line drawn from the sun through the eye of the observer. On one occasion four coloured luminous circles were observed. The exterior one might be twenty degrees in diameter. It exhibited all the colours of the spectrum. The next, a little within it, was of a whitish-gray colour; the third was only four or five degrees in diameter, and though it exhibited the colours of the spectrum, these colours were not very brilliant. The fourth was extremely beautiful and brilliant. The interior colour was yellow, then orange, red, violet, &c. The colours of the whole three coronæ were, I think, in the same order, but of this I am not very certain. Indeed, on reflection, I suspect that the second circle must have been in the reverse order of the first; the first and the fourth being the same. The third was not coloured. In the midst of these beautiful coronæ I observed my own shadow, the head surrounded by a glory. All the coronæ were evidently produced by the fog; my shadow was impressed on the surface of the sea."
The cause of these phenomena is "the reflection of the sun's rays, decomposed by different refractions in minute globules of water, of which the mist, wherein the coronæ occur, in a great measure appears to consist."Mock suns, or parhelia, are common appearances in northern skies. Sometimes two of these mock suns are seen, one on each side of their great original, glowing so brightly that either of them, if we could suppose it to have shone in the sky alone, would have made a very respectable sun indeed!
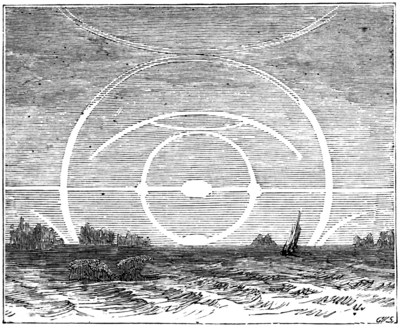
MOCK SUNS.
Even four of these "sun-dogs"—as they are sometimes called—have been seen surrounding the sun; one on each side of it, one directly above, and one immediately below, with a ring of light connecting them together, a streak of light passing horizontally and another passing perpendicularly between them, thus forming a luminous cross, in the centre of which was the sun itself. This magnificent spectacle is sometimes enhanced by a second circle of light enclosing the whole, and the edges of several outer circles springing in faint light therefrom until gradually lost, leaving the imagination to call up the idea of an endless series of glories extending over the whole sky.
Refraction frequently causes grotesque as well as wonderful and beautiful appearances. Ships are sometimes seen with their hulls flattened and their masts and sails drawn out to monstrous dimensions; or the hulls are heightened so as to appear like heavy castle walls, while the masts and sails are rendered ludicrously squat and disproportioned; and not only so, but ships are often seen with their images inverted over their own masts, so that to the observer it appears as if one ship were balancing another upside down—mast-head to mast-head. Land and icebergs assume the same curious appearances—peaks touching peaks, one set pointing upwards, the other set pointing down, while the broad bases are elevated in the air. At other times the whole mass of land and ice on the horizon is more or less broken up and scattered about as if in confusion, yet with a certain amount of regularity in the midst of it all, arising from the fact of every object being presented in duplicate, sometimes triplicate, and occasionally, though seldom, four-fold.
When sharp sudden frosts occur in those regions, the splendour of the scenery is still further enhanced by the formation of innumerable minute crystals which sparkle literally with as much lustrous beauty as the diamond. On one occasion Scoresby's ship was decorated with uncommon magnificence, and in a peculiarly interesting manner.
"In the course of the night," he writes, "the rigging of the ship was most splendidly decorated with a fringe of delicate crystals. The general form of these was that of a feather having half of the vane removed. Near the surface of the ropes was first a small direct line of very white particles, constituting the stem or shaft of the feather; and from each of these fibres, in another plane, proceeded a short delicate range of spiculæ or rays, discoverable only by the help of a microscope, with which the elegant texture and systematic construction of the feather were completed. Many of these crystals, possessing a perfect arrangement of the different parts corresponding with the shaft, vane, and rachis of a feather, were upwards of an inch in length, and three-fourths of an inch in breadth. Some consisted of a single flake or feather, but many of them gave rise to other feathers, which sprang from the surface of the vane at the usual angle. There seemed to be no limit to the magnitude of these feathers, so long as the producing cause continued to operate, until their weight became so great, or the action of the wind so forcible, that they were broken off, and fell in flakes to the deck of the ship."
It is impossible for the mind to conceive the effect of such a galaxy of curious, and bright, and eminently beautiful combinations as are sometimes displayed in the arctic regions. None of the fabulous conceptions of man, even though profoundly elaborated and brightly gilded with the coruscations of the most sparkling genius and fancy, ever produced so gorgeous a spectacle as may be witnessed there every summer day. Four or five suns in the blue sky, with lines and circles of light shooting from or circling round them! Ice in all its quaint, majestic, and shining forms, rendered still more quaint and grand by the influence of refraction; and, by the same power, ships sailing in the sky, sometimes, as if Nature's laws were abrogated, with their keels upwards, and their masts pointing to the sea! Walls of pure ice hundreds of feet high, many miles in extent, clear as crystal, and sending back the rays of heaven's luminaries in broad blazing beams; while the icebergs' pinnacles reflect them in sparkling points! White luminous fogs, like curtains of gauze, too thin to dim the general brightness, yet dense enough to invest the whole scene with a silver robe of mystery, and to refract the light and compel it to shine in great circles of prismatic colours! And everything—from the nature of the materials of which the gay scenery is composed—either white or blue, varying in all gradations from the fairest snow to the deepest azure, save where the rainbow's delicate hues are allowed to intermingle enough of pink, yellow, purple, orange, and green to relieve the eye and enable it more fully to appreciate the virgin drapery of the scene. All this, seen in detail—seen frequently in rapid succession—sometimes seen almost all at one moment,—all this is absolutely beyond conception, and utterly beyond adequate description. Yet all this is seen at times in those realms of ice and snow, which are, as we have already said, too much represented as the "gloomy, forbidding, inhospitable polar regions."
There are two sides to every picture. We take leave of this particular branch of our subject with the remark, that if the shady side of the far north is dreadfully dark and dreary, its bright side is intensely brilliant and beautiful.

![]()
This work was published before January 1, 1929, and is in the public domain worldwide because the author died at least 100 years ago.
Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse