the same rules which have been observed officially over a long period. Amongst these suggestions he advises that the blazoning of every coat or quarter should begin with a capital letter, and that, save on the occurrence of proper names, no other capitals should be employed. He also suggests that punctuation marks should be avoided as much as possible, his own practice being to limit the use of the comma to its occurrence after each tincture. He suggests also that figures should be omitted in all cases except in the numbering of quarterings.
When one or more quarterings occur, each is treated separately on its own merits and blazoned entirely without reference to any other quartering.
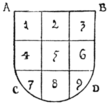
Fig. 63.—A to B, the chief; C to D, the base; A to C, dexter side; B to D, sinister side. A, dexter chief; B, sinister chief; C, dexter base; D, sinister base. 1, 2, 3, chief; 7, 8, 9, base; 2, 5, 8, pale; 4, 5, 6, fess; 5, fess point.
In blazoning a coat in which some quarterings (grand quarterings) are composed of several coats placed sub-quarterly, sufficient distinction is afforded for English purposes of writing or printing if Roman numerals are employed to indicate the grand quarters, and Arabic figures the sub-quarters. But in speaking such a method would need to be somewhat modified in accordance with the Scottish practice, which describes grand quarterings as such, and so alludes to them.
The extensive use of bordures, charged and uncharged, in Scotland, which figure sometimes round the sub-quarters, sometimes round the grand quarters, and sometimes round the entire escutcheon, causes so much confusion that for the purposes of blazoning it is essential that the difference between quarters and grand quarters should be clearly defined.
In order to simplify the blazoning of a shield, and so express the position of the charges, the field has been divided into points, of which those placed near the top, and to the dexter, are always considered the more important. In heraldry, dexter and sinister are determined, not from the point of view of the onlooker, but from that of the bearer of the shield. The diagram (Fig. 63) will serve to explain the plan of a shield's surface.
If a second shield be placed upon the fess point, this is called an inescutcheon (in German, the "heart-shield"). The enriching of the shield with an inescutcheon came into lively use in Germany in the course of the latter half of the fifteenth century. Later on, further points of honour were added, as the honour point (a, Fig. 64), and the nombril point (b, Fig. 64). These extra shields laid upon the others should correspond as much as possible in shape to the chief shield. If between the inescutcheon and the chief shield still another be inserted,

