Charnock, the founder of Calcutta, erected a bungalow and established a small bazaar here in 1689. The cantonment is situated on the left bank of the Hugli; it has also a large bazaar and several large tanks, and also a parade ground. To the south of the cantonment is situated the park, created by the taste and public spirit of Lord Wellesley. Within the park is situated the Government House, a noble building begun by Lord Minto, and enlarged into its present state by the marquess of Hastings. The park is beautifully laid out, and contains a small menagerie. Its most interesting feature is now Lady Canning’s tomb. Barrackpur played an important part in the two Sepoy mutinies of 1824 and 1857, but the details of these belong to the general history of British rule in India. North Barrackpur had a population in 1901 of 12,600 and south Barrackpur of 19,307.
Barrackpur subdivision was formed in 1904. It contains an area of 190 sq. m., which, at the census of 1901, had a population of 206,311, a large proportion being workers in the mills on the left bank of the Hugli.
BARRACKS (derived through the French from the Late Lat. barra, a bar), the buildings used for the accommodation of military or naval forces, including the quarters for officers, warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men, with their messes and recreation establishments, regimental offices, shops, stores, stables, vehicle sheds and other accessory buildings for military or domestic purposes. The term is usually applied to permanent structures of brick or stone used for the peace occupation of troops; but many hut barracks of corrugated iron lined with wood have been built, generally in connexion with a training ground for troops, and in these the accommodation given is somewhat less than in permanent barracks, and conditions more nearly approach those of a military encampment.
British System.—The accommodation to be given in British military barracks is scheduled in the Barrack Synopsis, which contains “statements of particulars, based upon decisions which have, from time to time, been laid down by authority, as regards the military buildings authorized for various units, and the accommodation and fittings to be provided in connexion therewith.” Each item of ordinary accommodation is described in the synopsis, and the areas and cubic contents of rooms therein laid down form the basis of the designs for any new barrack buildings. Supplementary to the synopsis is a series of “Standard Plans,” which illustrate how the accommodation may be conveniently arranged; the object of the issue of these plans is to put in convenient form the best points of previous designs, and to avoid the necessity of making an entirely fresh design for each building that is to be erected, by using the standard type modified to suit local conditions. External appearance is considered with regard to the materials to be used, and the position the buildings are to occupy; convenience of plan and sound sanitary construction being the principal objects rather than external effect, designs are usually simple, and depend for architectural effect more on the grouping and balance of the parts than on ornamentation such as would add to expense. The synopsis and standard plans are from time to time revised, and brought up to date as improvements suggest themselves, and increases in scale of accommodation are authorized, after due consideration of the financial effect; so that systematic evolution of barrack design is carried on.
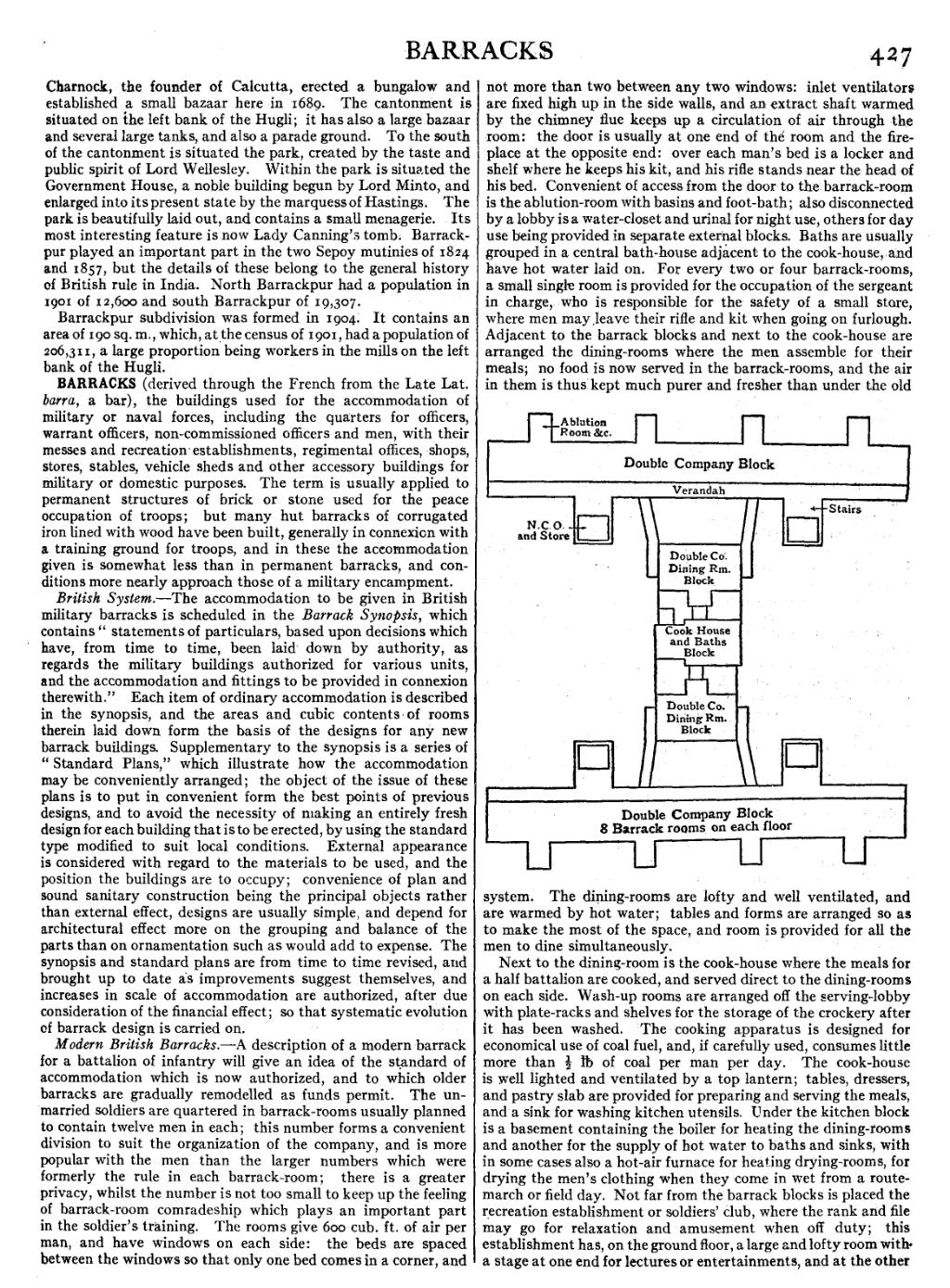
Modern British Barracks.—A description of a modern barrack for a battalion of infantry will give an idea of the standard of accommodation which is now authorized, and to which older barracks are gradually remodelled as funds permit. The unmarried soldiers are quartered in barrack-rooms usually planned to contain twelve men in each; this number forms a convenient division to suit the organization of the company, and is more popular with the men than the larger numbers which were formerly the rule in each barrack-room; there is a greater privacy, whilst the number is not too small to keep up the feeling of barrack-room comradeship which plays an important part in the soldier’s training. The rooms give 600 cub. ft. of air per man, and have windows on each side: the beds are spaced between the windows so that only one bed comes in a corner, and not more than two between any two windows: inlet ventilators are fixed high up in the side walls, and an extract shaft warmed by the chimney flue keeps up a circulation of air through the room: the door is usually at one end of the room and the fireplace at the opposite end: over each man’s bed is a locker and shelf where he keeps his kit, and his rifle stands near the head of his bed. Convenient of access from the door to the barrack-room is the ablution-room with basins and foot-bath; also disconnected by a lobby is a water-closet and urinal for night use, others for day use being provided in separate external blocks. Baths are usually grouped in a central bath-house adjacent to the cook-house, and have hot water laid on. For every two or four barrack-rooms, a small single room is provided for the occupation of the sergeant in charge, who is responsible for the safety of a small store, where men may leave their rifle and kit when going on furlough. Adjacent to the barrack blocks and next to the cook-house are arranged the dining-rooms where the men assemble for their meals; no food is now served in the barrack-rooms, and the air in them is thus kept much purer and fresher than under the old system. The dining-rooms are lofty and well ventilated, and are warmed by hot water; tables and forms are arranged so as to make the most of the space, and room is provided for all the men to dine simultaneously.

Next to the dining-room is the cook-house where the meals for a half battalion are cooked, and served direct to the dining-rooms on each side. Wash-up rooms are arranged off the serving-lobby with plate-racks and shelves for the storage of the crockery after it has been washed. The cooking apparatus is designed for economical use of coal fuel, and, if carefully used, consumes little more than 12 ℔ of coal per man per day. The cook-house is well lighted and ventilated by a top lantern; tables, dressers, and pastry slab are provided for preparing and serving the meals, and a sink for washing kitchen utensils. Under the kitchen block is a basement containing the boiler for heating the dining-rooms and another for the supply of hot water to baths and sinks, with in some cases also a hot-air furnace for heating drying-rooms, for drying the men’s clothing when they come in wet from a route-march or field day. Not far from the barrack blocks is placed the recreation establishment or soldiers’ club, where the rank and file may go for relaxation and amusement when off duty; this establishment has, on the ground floor, a large and lofty room with a stage at one end for lectures or entertainments, and at the other